
What Is Ethereum? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Understand what Ethereum is, how it works, the role of ETH and smart contracts, and the significance of Ethereum 2.0 in the evolving world of web3.
Ethereum is the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, following Bitcoin. However, its purpose extends beyond that of a digital currency. Launched in 2015, Ethereum is a decentralized computing platform that supports a broad range of applications, including financial services, games, and complex databases. It leverages blockchain technology to enable developers to create decentralized applications (dapps) that operate securely without intermediaries.
While Bitcoin was designed to serve primarily as digital money, Ethereum was developed with a different goal in mind. The platform was intended to provide a decentralized foundation for applications that require transparency, security, and reliability. According to the Ethereum Foundation, Ethereum can be used to codify, decentralize, secure, and trade just about anything. Today, Ethereum supports a growing ecosystem of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and other services within the web3 environment.

What Is Ethereum? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
How Ethereum Works
The Ethereum blockchain operates differently from Bitcoin’s blockchain. While Bitcoin’s network functions as a ledger for tracking transactions, Ethereum’s blockchain acts more like a decentralized computer. It maintains a record of transactions but also supports the creation and execution of applications. Developers use Ethereum’s infrastructure to build a wide variety of tools, including logistics management systems, games, and DeFi services that allow activities such as lending, borrowing, and trading without relying on traditional financial institutions.
At the center of Ethereum’s functionality are smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements where the terms are directly written into code. Once the conditions specified in the contract are met, it executes automatically. This automation removes the need for intermediaries and enhances security and efficiency across various applications.
The Ethereum network is maintained by thousands of nodes globally, ensuring that the platform remains decentralized and secure. To interact with the network, users pay fees in Ethereum’s native token, Ether (ETH), commonly referred to simply as Ethereum.
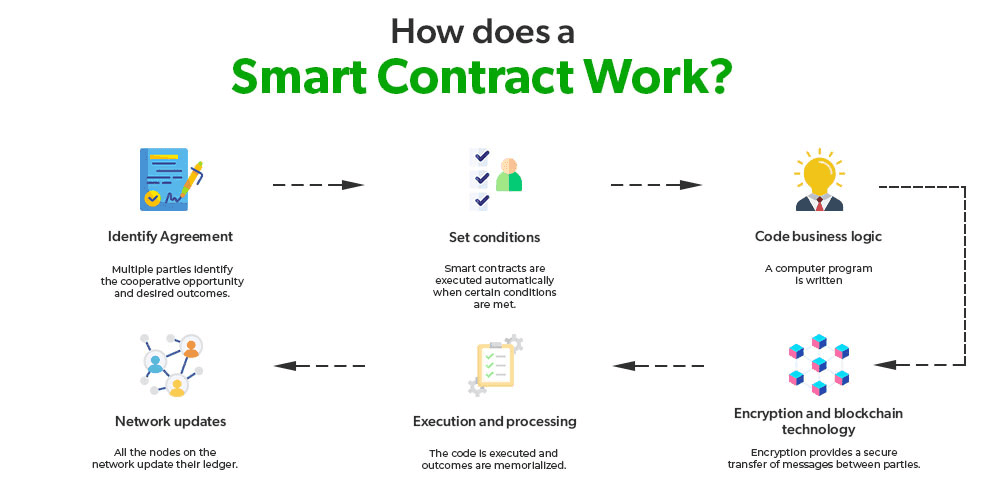
Whaat is a Smart Contract
Understanding Ethereum, Ether, and ETH
Ethereum refers to the network itself, while Ether is the native cryptocurrency used within the network. In everyday usage, the token is often called ETH. ETH can be sent, received, or stored similarly to Bitcoin, but it also serves a unique function within the Ethereum ecosystem by powering smart contract execution and other network activities. Fees paid for using the network are called "gas" and are denominated in ETH. In this sense, if Bitcoin is considered "digital gold," ETH can be seen as "digital oil," providing the fuel necessary to operate decentralized applications on the platform.
Is Ethereum Secure?
Ethereum’s security is largely attributed to its decentralized nature and its open-source framework. This allows independent researchers, computer scientists, and cryptographers to examine and test the network for vulnerabilities. As a result, the core Ethereum blockchain is considered secure.
However, the security of decentralized applications built on Ethereum can vary. Individual dapps may have coding flaws that could expose users to risks, including the potential loss of funds. While the code of many dapps is publicly available for review, these applications often have smaller user bases compared to Ethereum itself, meaning fewer eyes scrutinize their security. Users are encouraged to conduct thorough research before interacting with any decentralized application.

What Is Ethereum? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Ethereum’s Evolution to Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum initially relied on a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW) to validate transactions and maintain network security. PoW requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems in competition with each other, consuming significant computational power and energy. As Ethereum grew in popularity, PoW led to network congestion, high transaction fees, and environmental concerns due to its resource intensity.
To address these challenges, Ethereum transitioned to a new model called Ethereum 2.0, which was implemented in September 2022. Ethereum 2.0 introduced a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, aimed at making the network more scalable, secure, and energy-efficient. Under PoS, validators are chosen to verify transactions and create new blocks based on the amount of ETH they have staked, rather than through energy-intensive mining.

What is Proof of Stake
What Is Staking on Ethereum?
Staking is the process of participating in Ethereum’s Proof of Stake system by depositing ETH into a staking pool. Validators who stake ETH are selected to validate new transactions and are rewarded with additional ETH. The likelihood of being selected is proportional to the amount of ETH a validator has staked and the duration of the stake.
Validators are incentivized to act honestly because malicious behavior could result in the loss of their staked ETH. Once a validator proposes a block, other validators review and attest to its accuracy. When a sufficient number of attestations are gathered, the block is added to the blockchain, and the validators receive rewards based on their stakes.
The Role of Smart Contracts on Ethereum
Smart contracts are a central innovation of the Ethereum platform. The concept was first introduced by Nick Szabo in the 1990s. Szabo compared smart contracts to a vending machine that automatically dispenses a product when payment is received, illustrating how agreements can be enforced without human intervention.
On Ethereum, smart contracts facilitate a wide range of transactions and services. They operate autonomously, reducing the need for intermediaries and lowering the risk of fraud. Smart contracts can underpin decentralized finance applications, marketplaces, and even voting systems, contributing to the broader growth of web3.
How to Buy Ethereum
Acquiring ETH involves a few fundamental steps. Each Ethereum address is associated with a public key and a private key. The public key functions like an email address where ETH and Ethereum-based tokens can be received. The private key, which must be kept secure, provides access to the holdings.
A digital wallet is necessary to store and manage ETH. Beginners often start with custodial wallets provided by cryptocurrency exchanges like Coinbase, where the platform manages the private keys on behalf of the user. More experienced users might prefer non-custodial wallets, which offer greater control over private keys and direct interaction with decentralized applications.
Purchasing ETH can be done using fiat currencies such as dollars, euros, or yen through cryptocurrency exchanges. It is important for users to understand the responsibility that comes with managing private keys, as losing access to them can result in the permanent loss of funds.

What Is Ethereum? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
How Ethereum Gains Value
Ethereum’s market value, like that of other assets, is determined by supply and demand dynamics across global trading platforms. However, its broader utility contributes significantly to its valuation. Ethereum supports a growing ecosystem of decentralized applications, stablecoins, and DeFi services. This expansion drives demand for ETH, as it is needed to power transactions and smart contract executions.
Moreover, the introduction of Ethereum 2.0 has improved network efficiency, potentially attracting more developers and users. As usage increases, transaction fees paid in ETH add to the token’s overall demand, influencing its market price.
Conclusion
Ethereum plays a foundational role in the development of decentralized technologies and the broader web3 ecosystem. Its unique combination of a flexible blockchain, support for smart contracts, and the recent transition to a more sustainable Proof of Stake model positions it as a key platform for innovation. As decentralized finance, applications, and services continue to grow, Ethereum remains at the center of the movement toward a more open and accessible digital economy.
Source: Coinbase
About the author
Eliza Crichton-Stuart
Head of Operations
Updated:
April 28th 2025
Posted:
April 28th 2025


