What Are Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
Learn about Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs), how they operate through smart contracts, their advantages, challenges, and examples of DAOs in real-world applications.
By Eliza Crichton-Stuart
Updated April 28th 2025
Updated April 28th 2025

Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are an emerging form of organization built on blockchain technology, designed to operate without a central leadership structure. Instead of being governed by a traditional management hierarchy, DAOs are managed by a community that collaborates around a shared objective.
The operational rules of a DAO are enforced through blockchain-based smart contracts, making the organization transparent and resistant to centralized control. As a result, DAOs are seen as a key development within the broader web3 landscape, offering new ways for communities to organize and manage collective resources.

What Are Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
How DAOs Operate
DAOs rely on smart contracts to function. These smart contracts are pieces of code deployed on a blockchain that automatically execute specific actions when certain predefined conditions are met. The smart contracts define the rules of the organization and the parameters by which decisions can be made. Members of a DAO typically hold governance tokens that allow them to vote on proposals concerning the organization's direction and activities.
In most DAOs, a proposal is only enacted if it receives the required level of support from token holders, ensuring that the community collectively influences important decisions. The exact rules regarding proposal creation, voting periods, and quorum thresholds vary by DAO and are coded directly into their underlying smart contracts.

Input and Output via Blockchain
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
DAOs offer several potential advantages that make them an attractive model for certain communities and projects. One of the most significant benefits is the decentralization of power. Unlike traditional organizations, where a central authority makes decisions on behalf of stakeholders, DAOs distribute decision-making among all token holders.
This model can increase transparency, as all rules, decisions, and financial transactions are recorded on an open blockchain. Furthermore, DAOs remove the need for intermediaries, allowing members to collaborate and allocate resources more efficiently. In the context of web3, DAOs align with broader goals of promoting open, decentralized, and user-controlled systems.
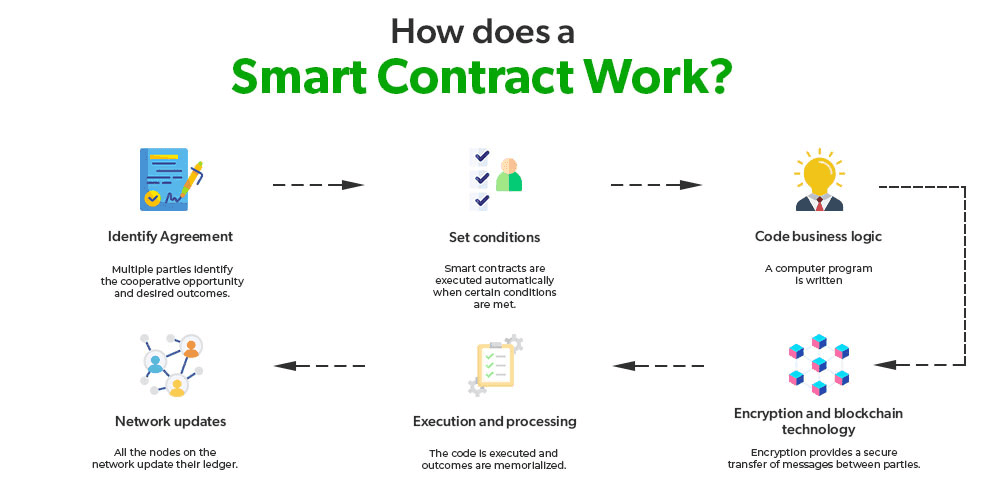
How Does Smart Contracts Work
Challenges and Limitations of DAOs
Despite their potential, DAOs also face a range of challenges. One of the most pressing concerns is security. If a smart contract governing a DAO contains vulnerabilities, malicious actors could exploit these weaknesses to access or drain treasury funds. The history of DAOs includes notable incidents where security flaws led to significant financial losses.
Additionally, while DAOs aim to promote decentralization, the distribution of governance tokens can sometimes become uneven, allowing a small number of participants to accumulate significant voting power. This concentration of influence can undermine the democratic ideals that DAOs seek to promote. Ensuring fair participation and protecting against security threats remain ongoing concerns for DAO developers and communities.

Smart Contract Example
Examples of DAOs in Practice
Several real-world examples illustrate both the promise and the risks associated with DAOs. One of the earliest and most prominent examples was The DAO, an organization created to facilitate venture capital funding using blockchain technology. However, shortly after its launch, a vulnerability was exploited, leading to a significant loss of funds and sparking widespread debate about DAO security.
More recently, ConstitutionDAO demonstrated the ability of a decentralized group to mobilize quickly around a common goal. Although the group ultimately failed in its attempt to purchase a rare copy of the U.S. Constitution, it showed that DAOs could rapidly organize resources and attention toward ambitious projects.
Final Thoughts
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations represent a new model of governance that leverages blockchain technology to promote transparency, autonomy, and community-driven decision-making. Operating within the web3 environment, DAOs continue to evolve, offering innovative approaches to organizing collective action without traditional hierarchies. However, they also face significant challenges related to security and the equitable distribution of governance power. As DAOs continue to develop and mature, their role in shaping the future of decentralized systems will likely expand, offering new possibilities and lessons for digital governance.
Source: Coinbase
updated:
April 28th 2025
posted:
April 27th 2025


