Nintendo’s Switch 2 pre-order activity is providing new evidence that video games maintain economic resilience even during periods of financial strain. According to data from SuperJoost, this week 2.2 million Japanese consumers registered for a Switch 2 lottery, highlighting significant demand for a premium-priced $449.99 console despite the presence of elevated tariffs and ongoing global economic uncertainty.
Counter-Cyclical Trends
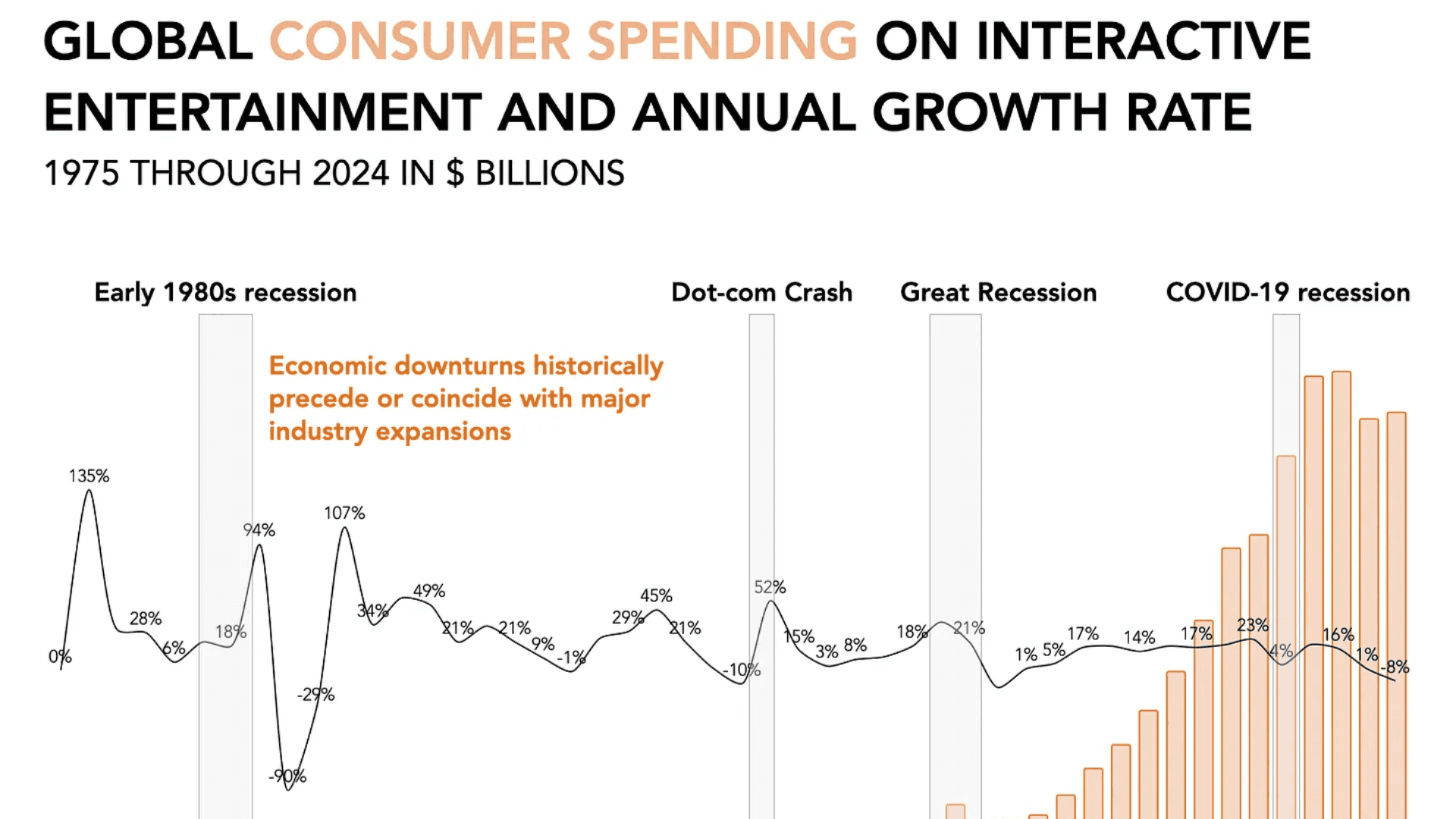
The scale of consumer interest reflects more than the anticipation surrounding a new product launch. It underscores a counter-cyclical trend within the gaming sector. Historically, video games have demonstrated remarkable stability during economic downturns. During the 2007–2009 financial recession, global gaming revenues remained stable, growing slightly from $61.3 billion in 2007 to $62.7 billion in 2010, while most other discretionary spending categories contracted sharply.

Millions of Gamers Registered for Switch 2 Lottery
Historical Patterns of Gaming Stability
Hardware sales during the late-2000s recession further reinforce the industry's resilience. Sales of the Wii, Xbox 360, PlayStation 3, and Nintendo DS all posted positive unit growth, even as economic conditions worsened. The Wii became notably scarce due to overwhelming demand, while the PlayStation 3, despite initial pricing challenges, achieved a strong recovery. These patterns contradict traditional economic forecasts, which generally predict that durable goods suffer during recessions.
Consumer engagement with gaming also increased during periods of financial stress. Nielsen reported that weekly gameplay hours rose from 15 to 18 hours as economic conditions deteriorated. Popular titles such as World of Warcraft reached peak engagement levels, indicating that consumers shifted both time and money toward interactive entertainment experiences, which offered more value for each hour spent compared to alternative leisure activities.
This trend continued during the COVID-19 pandemic. Entertainment’s share of household spending climbed to 5.6% during the recession, compared to 4.9% in 2013. By 2023, the figure adjusted to 4.7%, still above pre-pandemic norms. The data suggests that a durable recalibration of consumer priorities continues to favor interactive entertainment, even during economic downturns.

Statista: Consumer Games Spending During Covid
Strategic Pricing Amid Economic Uncertainty
Sony’s recent strategy reinforces the idea that premium pricing can be sustained even during financial hardship. The company increased PlayStation 5 retail prices in markets such as Europe, Australia, and New Zealand, citing inflation and currency volatility. Despite initial concerns, Sony’s move mirrored Nintendo’s approach of maintaining strong pricing during challenging times.
Sony’s most recent earnings report reflected the success of this strategy. The gaming division recorded $11.2 billion in revenue, a 16% year-over-year increase, and operating income rose 37% to a record $787 million. These results were driven by strong hardware performance and higher-margin services offered through the PlayStation Network. The company's ability to sustain high demand and profitability amid inflationary pressures supports the broader notion that gaming remains a resilient industry.
Nintendo’s positioning with the Switch 2 reflects a calculated approach to recent import tariffs. The company’s pricing structure aims to buffer against added costs without significantly dampening consumer demand. Nintendo’s consistent focus on brand value and limited discounting practices have conditioned its audience to prioritize quality and experience over price, reinforcing relatively inelastic demand.

Nintendo’s Hardware Sales 2006-2024
Managing Supply and Brand Strength
Nintendo’s use of a lottery system for Switch 2 pre-orders exemplifies strategic supply management. By controlling early product availability, the company preserves pricing power, gathers early demand data, and maintains a sense of exclusivity. This approach supports the company’s broader strategy of sustaining premium brand positioning as the industry shifts from a content innovation phase to a distribution innovation phase.
Previous cycles, including recoveries following the 1983 crash, the 2008 recession, and the COVID-19 pandemic, have demonstrated that the gaming industry oscillates between focusing on game content creation and business model innovation. As macroeconomic indicators soften once again, companies with strong digital distribution frameworks are better positioned to succeed.
Broader Implications for Gaming Industry
The intersection of tariff pressures and distribution innovation could accelerate the restructuring of the gaming economy. While current signals, such as extraordinary demand for the Switch 2 in Japan, suggest continued strength for premium content providers like Nintendo, historical patterns point to the potential for significant shifts toward alternative distribution models, such as subscription services and cloud gaming.
The gaming industry is not completely insulated from global economic volatility, but historical evidence shows that it tends to be more resilient than many other sectors. Companies that have transitioned successfully toward digital distribution, such as Electronic Arts and Take-Two Interactive, benefit from stronger insulation against tariffs and economic fluctuations. These companies generate over 80% of their revenues through digital channels, compared to firms that rely on physical goods like tabletop games, which face increasing challenges.
As the digital economy continues to evolve, Nintendo’s strategy offers a case study in sustainable business adaptation. By balancing brand strength, strategic pricing, and supply management, Nintendo provides insights that extend beyond gaming into broader considerations for digital business strategy during periods of economic transition.
Source: SuperJoost